Cdk7 Rabbit mAb [C634]Cat NO.: A66515
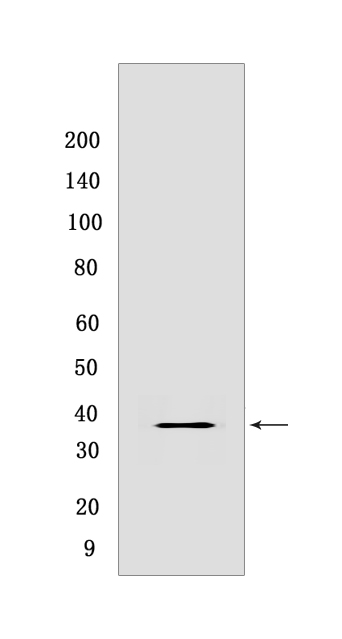
Western blot(SDS PAGE) analysis of extracts from Raw 264.7 cells.Using Cdk7Rabbit mAb [C634] at dilution of 1:1000 incubated at 4℃ over night.
Product information
Protein names :CDK7,CAK,CAK1,CDKN7,MO15,STK1,CDK7_HUMAN,Cyclin-dependent kinase 7
UniProtID :P50613
MASS(da) :39,038
MW(kDa) :39 kDa
Form :Liquid
Purification :Protein A purification
Host :Rabbit
Isotype :IgG
sensitivity :Endogenous
Reactivity :Human,Mouse,Rat
- ApplicationDilution
- 免疫印迹(WB)1:1000-2000
- 免疫组化(IHC)1:100
- The optimal dilutions should be determined by the end user
Specificity :Antibody is produced by immunizing animals with a synthetic peptide at the sequence of human Cdk7
Storage :Antibody store in 10 mM PBS, 0.5mg/ml BSA, 50% glycerol. Shipped at 4°C. Store at-20°C or -80°C. Products are valid for one natural year of receipt.Avoid repeated freeze / thaw cycles.
WB Positive detected :Raw 264.7 cells
Function : Serine/threonine kinase involved in cell cycle control and in RNA polymerase II-mediated RNA transcription. Cyclin-dependent kinases (CDKs) are activated by the binding to a cyclin and mediate the progression through the cell cycle. Each different complex controls a specific transition between 2 subsequent phases in the cell cycle. Required for both activation and complex formation of CDK1/cyclin-B during G2-M transition, and for activation of CDK2/cyclins during G1-S transition (but not complex formation). CDK7 is the catalytic subunit of the CDK-activating kinase (CAK) complex. Phosphorylates SPT5/SUPT5H, SF1/NR5A1, POLR2A, p53/TP53, CDK1, CDK2, CDK4, CDK6 and CDK11B/CDK11. CAK activates the cyclin-associated kinases CDK1, CDK2, CDK4 and CDK6 by threonine phosphorylation, thus regulating cell cycle progression. CAK complexed to the core-TFIIH basal transcription factor activates RNA polymerase II by serine phosphorylation of the repetitive C-terminal domain (CTD) of its large subunit (POLR2A), allowing its escape from the promoter and elongation of the transcripts (PubMed:9852112). Phosphorylation of POLR2A in complex with DNA promotes transcription initiation by triggering dissociation from DNA. Its expression and activity are constant throughout the cell cycle. Upon DNA damage, triggers p53/TP53 activation by phosphorylation, but is inactivated in turn by p53/TP53,this feedback loop may lead to an arrest of the cell cycle and of the transcription, helping in cell recovery, or to apoptosis. Required for DNA-bound peptides-mediated transcription and cellular growth inhibition..
Tissue specificity :Ubiquitous.
Subcellular locationi :Nucleus. Cytoplasm. Cytoplasm, perinuclear region.
IMPORTANT: For western blots, incubate membrane with diluted primary antibody in 1% w/v BSA, 1X TBST at 4°C overnight.